What are the requirements for obtaining a license for operating a food business for a company?

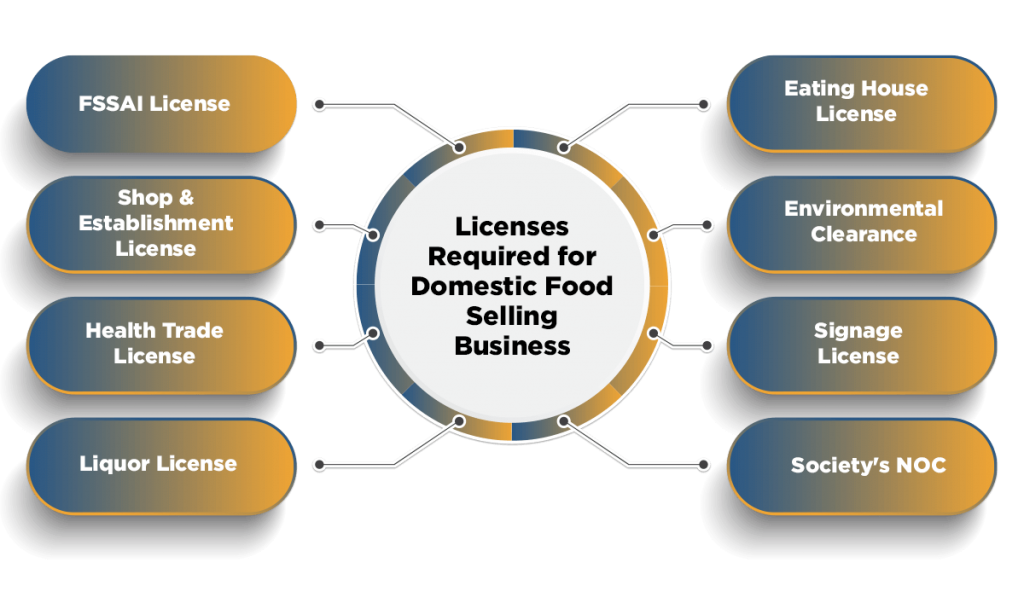
 REQUIREMENTS 1. Understanding Regulatory Frameworks:
REQUIREMENTS 1. Understanding Regulatory Frameworks:

Before delving into the specifics of licensing, it's crucial to understand the regulatory frameworks governing food businesses. These regulations are designed to ensure public health and safety by establishing standards for food production, handling, and distribution. In the United States, for instance, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) oversee food safety regulations, while in the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets guidelines for member states.
2. Determine Business Type and Activities:
The requirements for a food business license can vary based on the type of food business and the activities involved. Businesses may fall into categories such as restaurants, food trucks, catering services, food manufacturing, or retail food establishments. Each category may have specific regulations that need to be adhered to, such as kitchen requirements, storage conditions, and transportation standards.
3. Business Registration and Permits:
Before applying for a food business license, the company must be properly registered with the relevant authorities. This may involve obtaining a business license or permit from the local government or municipal authority. Additionally, specific permits may be required for activities such as selling food in public spaces, operating a mobile food truck, or serving alcohol.
4. Facility Requirements:
Food businesses must operate in facilities that meet certain standards for cleanliness, sanitation, and food safety. This includes having adequate kitchen facilities with proper equipment for food preparation, cooking, and storage. Facilities may be subject to regular inspections by health authorities to ensure compliance with hygiene and safety standards.
5. Food Safety Training and Certification:
Employees involved in food handling, preparation, and service must undergo food safety training to ensure they understand proper hygiene practices, safe food handling techniques, and potential hazards related to foodborne illnesses. In many jurisdictions, at least one employee must be certified in food safety management, such as through the ServSafe program in the United States.
6. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) Plan:
Many food businesses are required to develop and implement a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan to identify and mitigate food safety risks throughout the production process. This involves conducting a thorough analysis of potential hazards, establishing critical control points, implementing control measures, and monitoring procedures to ensure food safety.
7. Food Labeling and Packaging Requirements:
Food products must be labeled accurately and comply with regulations regarding ingredient listing, nutritional information, allergen declarations, and expiration dates. Packaging materials must also meet safety standards to prevent contamination and ensure product integrity during storage and transportation.
8. Compliance with Health Codes and Regulations:
Food businesses must comply with local health codes and regulations, which may include requirements related to food storage temperatures, sanitation practices, waste disposal, and pest control. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in fines, closure orders, or legal action.
9. Environmental Health Permits:
Depending on the nature of the food business and its impact on the environment, additional permits may be required. This could include permits for wastewater discharge, air quality compliance, or hazardous materials handling, especially for food manufacturing facilities.
10. Regular Inspections and Compliance Monitoring:
After obtaining a food business license, companies are typically subject to regular inspections by health authorities to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements. Inspections may occur annually or more frequently, depending on the level of risk associated with the business activities.
11. Record-Keeping and Documentation:
Food businesses are often required to maintain detailed records and documentation related to food safety practices, employee training, supplier information, and inspection reports. This information may need to be provided to regulatory authorities upon request to demonstrate compliance with regulations.
12. Renewal and Updating of Licenses:
Food business licenses are typically valid for a specified period, after which they must be renewed to continue operating legally. Renewal requirements may include updating documentation, attending refresher training courses, or undergoing additional inspections.
 Conclusion:
Conclusion:

Obtaining a license for operating a food business involves navigating a complex landscape of regulations, permits, and requirements designed to ensure food safety and public health. By understanding and complying with these requirements, companies can establish and maintain successful food businesses while meeting their legal obligations. It's essential to stay informed about evolving regulations and best practices to adapt to changing requirements and industry standards. Additionally, seeking guidance from legal professionals or regulatory consultants can help navigate the intricacies of the licensing process and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.


1. Research and Planning:
Before starting the process, conduct thorough research to understand the regulatory requirements specific to your jurisdiction and the type of food business you intend to operate. Identify the necessary permits, licenses, and regulations applicable to your business activities.
2. Business Registration:
Ensure that your company is properly registered with the relevant authorities. This may involve registering your business with the appropriate government agency or municipality and obtaining a business license or permit.
3. Facility Preparation:
Prepare your food establishment to meet regulatory standards for cleanliness, sanitation, and food safety. This may include ensuring proper kitchen facilities, equipment, storage areas, and waste disposal systems. Make any necessary renovations or improvements to comply with health and safety regulations.
4. Develop Food Safety Plan:
Develop a comprehensive food safety plan, which may include a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan. Identify potential food safety hazards, establish critical control points, implement control measures, and establish monitoring procedures to ensure food safety throughout the production process.
5. Employee Training:
Provide food safety training for all employees involved in food handling, preparation, and service. Ensure that employees understand proper hygiene practices, safe food handling techniques, and the importance of following food safety protocols. At least one employee may need to be certified in food safety management.
6. Obtain Necessary Permits and Licenses:
Apply for the required permits and licenses to operate your food business. This may include a food service license, health permit, alcohol license (if applicable), zoning permit, signage permit, and any other permits required by local regulations. Submit all necessary documentation and fees as required.
7. Food Labeling and Packaging:
Ensure that all food products are labeled accurately and comply with regulations regarding ingredient listing, nutritional information, allergen declarations, and expiration dates. Packaging materials should also meet safety standards to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity.
8. Compliance with Health Codes:
Comply with local health codes and regulations governing food safety, sanitation practices, food storage temperatures, waste disposal, and pest control. Regularly inspect your premises to ensure compliance with these regulations and address any issues promptly.
9. Environmental Health Permits:
Obtain any additional permits required for environmental health compliance, such as permits for wastewater discharge, air quality compliance, or hazardous materials handling, especially for food manufacturing facilities.
10. Regular Inspections:
Prepare for and undergo regular inspections by health authorities to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements. Address any deficiencies identified during inspections promptly to maintain compliance and prevent fines or penalties.
11. Record-Keeping:
Maintain detailed records and documentation related to food safety practices, employee training, supplier information, inspection reports, and permits/licenses. Keep these records organized and up-to-date, as they may need to be provided to regulatory authorities upon request.
12. License Renewal:
Renew your food business license and permits as required by your jurisdiction. Stay informed about renewal deadlines and any updates to regulations or requirements that may affect your business operations. Update documentation, attend refresher training courses, and undergo additional inspections as needed for license renewal.
By following these steps and staying diligent in compliance
with regulatory requirements, you can successfully obtain a license for operating
a food business for your company and ensure the safety and satisfaction of your
customers.
Related Articles
Starting a Home-Based Business in Mumbai: Legal Requirements
Mumbai, India’s financial capital, is home to countless entrepreneurs who dream of running their own businesses. With the rise of freelancing, online selling, consulting, and creative ventures, home-based businesses have become a popular way to begin ...How to Start a New Business; Step by Step Guide
How to Start a Business: A Step-by-Step Guide Starting a new small business? Find out where to begin and how to achieve success. You want to make sure you prepare thoroughly before starting a business, but realize that things will almost certainly go ...How To Start New Business for Food
Starting a new food business can be an exciting and rewarding endeavour, but it also requires careful planning and execution to be successful. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to start a food business: 1. Identify Your Niche and Concept: Determine ...How To Start New Business for Food
Introduction Starting a food business combines passion with entrepreneurship. Unlike many industries, food resonates emotionally—fueling comfort, nostalgia, community, and culture. Whether it’s a cherished family recipe, a revolutionary product, or a ...HOW TO START A RESTAURANT/ FOOD BUSINESS IN INDIA
The Indian Restaurant Market is one of the fastest-growing in the world. It is growing at a compounded annual growth rate of 9 percent, as per the National Restaurant Association of India (NRAI) report. Despite the hardships and challenges faced by ...