What is GST Audit?
Audit under GST involves examination of records, returns and other documents maintained by a GST registered person. It also ensures correctness of turnover declared, taxes paid, refund claimed, input tax credit availed and assess other such compliances under GST Act to be checked by an authorized expert.
GST is a trust-based taxation regime wherein a taxpayer is required to self-assess his tax liability, pay taxes and file returns. Thus, to ensure whether the taxpayer has correctly self -assessed his tax liability a robust audit mechanism is a must. Various measures are taken by the government for proper implementation of GST and audit is one amongst them.
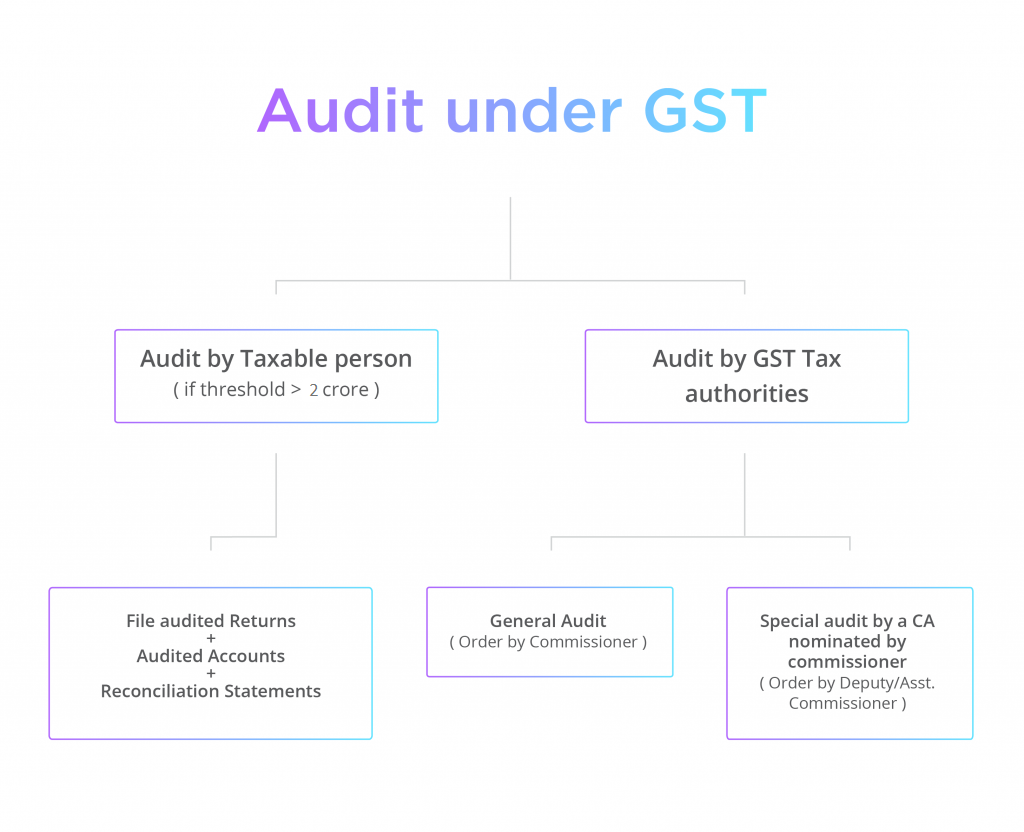
Types of GST Audit
| Types |
Performed By |
When Initiated |
| Turnover based Audit |
Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant appointed by the taxpayer |
If the Turnover exceeds 2 crores^ the taxpayer has to get his accounts & records audited |
| Normal audit/General Audit |
Commissioner of CGST/SGST or any Officer authorized by him |
On order of Commissioner by giving 15 days prior notice |
| Special audit |
A Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant, nominated by Commissioner |
On order of Deputy/Assistant Commissioner with prior approval of Commissioner |
Turnover-based Audit under Section 35(5) of CGST Act
If the annual turnover of a registered taxpayer is more than Rs. 2 crores^ in a financial year , he is required to get his accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant every year.
A financial year covers the 12-month period beginning from April of a calendar year to March of the next calendar year.
Special Note: For the purpose of finding out the turnover limit for Financial Year 2017-18, it has been clarified in the government’s press release dated 3rd July 2019. It shall cover the period 1st July 2017 to 31st March 2018 and excludes the first quarter of FY 2017-18.
Aggregate turnover is calculated as follows:
Aggregate turnover = Value of all taxable (inter-state and intra-state) supplies + exempt supplies + export supplies of all goods and service
The total turnover calculation must be PAN-based, which means that once the turnover under the PAN is more than Rs. 2 crores^ all business entities registered under GST for that PAN will be liable for GST audit for a financial year.
- All taxable (inter-state and intra-state) supplies other than supplies on which reverse charge is applicable
- Supplies between separate business verticals.
- Goods supplied to/received from job worker on principal to principal basis.
- Value of all export/zero-rated supplies.
- Supplies of agents/ job worker on behalf of the principal.
- All exempt supplies. E.g. Agricultural produce supplied along with branded ready-to-eat food.
- All taxes other than those covered under GST Eg: Entertainment Tax paid on the sale of movie tickets.
- Inward supplies on which tax is paid under reverse charge.
- All taxes and cess charged under Goods and Service Tax like CGST, SGST or IGST, Compensation Cess.
- Goods supplied to or received back from a Job Worker.
- Activities which are neither supply of goods nor service under schedule III of CGST Act.
Audit under GST
Audit under GST is the process of examination of records, returns and other documents maintained by a taxable person. The purpose is to verify the correctness of turnover declared, taxes paid, refund claimed and input tax credit availed, and to assess the compliance with the provisions of GST.
Every registered taxable person whose turnover during a financial year exceeds the prescribed limit [as per the latest GST Rules, the turnover limit is above Rs 2 crore^] shall get his accounts audited by a chartered accountant or a cost accountant. He shall electronically file:
- an annual return using the Form GSTR 9 by 31st December of the next Financial Year* ,
- the audited copy of the annual accounts,
- a certified reconciliation statement in the form GSTR-9C, reconciling the value of supplies declared in the return with the audited annual financial statement,
- and other particulars as prescribed.
For businesses with an annual turnover of less than Rs 5 crore, filing of GSTR-9C for FY 2018-19 has been waived off.
Rectifications to Returns After GST Audit
If any taxable person, after furnishing a return discovers any omission/incorrect details (from results of audit), he can rectify subject to payment of interest. However, no rectification will be allowed after the due date for filing of return for the month of September or second quarter, (as the case may be), following the end of the financial year, or the actual date of filing o the relevant annual return, whichever is earlier.
For example, X found during the audit that he has made a mistake in Oct 2017 return. X submitted an annual return for FY 2017-18 on 31st August 2018 along with audited accounts. He can rectify the Oct 2017 mistake within-
20th Oct 2018 (last date for filing Sep return)
or
31st August 2018 ( the actual date of filing of relevant annual return)
-earlier, ie., his last date for rectifying is 31st August 2018.
This rectification will not be allowed where results are from scrutiny/audit by the tax authorities.
Audit by Tax Authorities

- The Commissioner of CGST/SGST (or any officer authorized by him) may conduct an audit of a taxpayer. The frequency and manner of an audit will be prescribed later.
- A notice will be sent to the auditee at least 15 days before.
- The audit will be completed within 3 months from the date of commencement of the audit.
- The Commissioner can extend the audit period for a further six months with reasons recorded in writing.
The taxable person will be required to:
- provide the necessary facility to verify the books of account/other documents as required
- to give information and assistance for timely completion of the audit.
On conclusion of an audit, the officer will inform the taxable person within 30 days of:
- the findings,
- their reasons, and
- the taxable person’s rights and obligations
If the audit results in detection of unpaid/short paid tax or wrong refund or wrong input tax credit availed, then demand and recovery actions will be initiated.
When can a special audit be initiated?
The Assistant Commissioner may initiate the special audit, considering the nature and complexity of the case and interest of revenue. If he is of the opinion during any stage of scrutiny/ inquiry/investigation that the value has not been correctly declared or the wrong credit has been availed then special audit can be initiated.
A special audit can be conducted even if the taxpayer’s books have already been audited before.
Who will order and conduct a special audit?
The Assistant Commissioner (with the prior approval of the Commissioner) can order for special audit (in writing). The special audit will be carried out by a chartered accountant or a cost accountant nominated by the Commissioner.
Time limit for special audit
The auditor will have to submit the report within 90 days. This may be further extended by the tax officer for 90 days on an application made by the taxable person or the auditor.
Cost
The expenses for examination and audit including the auditor’s remuneration will be determined and paid by the Commissioner.
Findings of special audit
The taxable person will be given an opportunity of being heard in findings of the special audit.
If the audit results in detection of unpaid/short paid tax or wrong refund or input tax credit wrongly availed then demand and recovery actions will be initiated.
Thus, GST is a completely new tax regime already taking India by storm. Businesses will face challenges in transition and application of GST. To know more about GST, feel free to read more of our articles on our blog.
Only a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant can perform a GST Audit u/s 35.
Points to Note:
- An internal auditor cannot parallelly be appointed as a GST Auditor.
- The GST Act does not allow a GST practitioner to perform the audit. The power to audit is granted only to a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant who is in practice or is an employee of a firm of Chartered Accountants or Cost Accountants. Therefore, a Chartered Accountant must not be registered as a GST practitioner for the purpose of issuing the Audit Report.
- Where an organisation or an entity has multiple branches registered under GST in different states/UTs, the total aggregate turnover of all such branches is considered while calculating the threshold limit of Rs. 2 crores^.So, if the cumulative turnover of all the branches exceeds Rs. 2 crores^, then the GST audit is applicable to each of these branches, irrespective of whether the turnover of a particular branch is less than the threshold.In such cases, one can appoint either one dedicated auditor for all branches or separate auditor for each branch. Where multiple branches have different auditors, the Standards on Auditing: SA 299 — Responsibility of the Joint Auditors may apply for the purpose of reporting GST Audit observations & Reporting.
For businesses with an annual turnover of less than Rs 5 crore, filing of GSTR-9C for FY 2018-19 is waived off.
Appointment of GST Auditor:
A proprietor, partner or Board of Directors in case of a Company should appoint a GST Auditor at the beginning of the financial year.
Following are important accounts or records for review:
- Sales Register
- Stock Register
- Purchase Register and Expenses ledgers
- Input tax credit availed and utilized
- Output tax payable and paid
- E-way bills generated during the period under Audit, if in compliance with rules.
- Any documents that record communications from the GST department relating to the year.
Forms for Annual return and GST Audit:
| Type of taxpayer |
Form to be filed |
| Whether or not applicable to GST Audit |
|
| A Regular taxpayer filing GSTR 1 and GSTR 3B |
GSTR-9 |
| A Taxpayer under Composition Scheme |
GSTR-9A |
| E-commerce operator |
GSTR-9B |
| Applicable for GST Audit |
|
| Taxpayers whose turnover exceeds Rs. 2 crores^ in FY |
GSTR-9C |
The Auditor must report any tax liability pending for payment by the taxpayer, identified through the reconciliation exercise and observations made on GST audit. Taxpayers can settle taxes as recommended by the auditor in Form DRC-03.
Submission of GST Audit report & Annual return:
The finalized GSTR-9C can be certified by the same CA who conducted the GST audit or it can also be certified by any other CA who did not conduct the GST Audit for that particular GSTIN.
The following must be reported and certified by the GST Auditor or the certifier:
- Whether or not all the requisite accounts or records are maintained.
- Whether or not the Financial Statements are prepared as per the books of accounts maintained at the principal place of business or additional place of business of the taxpayer.
- Certify the accuracy of information in GSTR-9C.
- To list down the audit observations or reservations or comments, if any.
^For businesses with an annual turnover of less than Rs 5 crore, filing of GSTR-9C for FY 2018-19 is waived off.
Documents to be furnished by the taxpayer:
- Audited financial statements (which is PAN-based)
- Annual return in form GSTR-9 (for every GSTIN)
- Certified reconciliation statement in Form GSTR-9C, reflecting reconciled values of supplies and tax amounts declared in GSTR-9 compared to audited financials in Part-A, along with the Audit report in Part-B.
GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C are due on or before 31st December* of the subsequent fiscal year.
Special Note: *GSTR-9 filing for businesses with turnover up to Rs 2 crore^ made optional for FY 2017-18 and FY 2018-19.
There is no specific provision. Hence, it is subject to a general penalty of Rs.25,000.
For businesses with an annual turnover of less than Rs 5 crore, filing of GSTR-9C for FY 2018-19 is waived off.
Related Articles
GST Compliance due dates in India
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax system that has transformed India's taxation landscape. It has replaced multiple indirect taxes levied by the central and state governments, streamlining the taxation process and fostering ease of doing ...Important Due Dates For GST Returns Filing
Important GST Dates – GST Calendar 2021- 2022 GST calendar helps every registered business and professionals to be ready for compliance well in advance. GST Dates are crucial for every taxpayer to file the GST returns and prescribed forms under the ...Penalty for Late Filing of GST Return
What is GST Return Form? GST Return Form is a document containing details of all purchases, sales, output GST (on sales) and input tax credit (GST paid on purchases) to calculate an assessee’s GST liability for a particular tax period. Currently GST ...what are the GST Departmental Audit Applicability?
GST Departmental Audit GST has been one of the biggest tax reforms of our country. July 2021 marked four years of GST Implementation and though it has stabilized to a large extent, the taxpayers are still grappling with some issues and compliances ...What is the Turnover Limit for GST Audit?
As per the Finance Act, 2021, the requirement of GST audit and submission of GSTR-9C as certified by the CA/CMA was removed. As per the 43rd GST Council meeting that was held on 28th May 2021, the GST Council recommended that GSTR-9C may be still ...