GST Audit Procedure by Different Authorities
Goods and Service Tax (GST) is structured for efficient tax collection, reduction in corruption, easy inter-state movement of goods and a lot more.
The GST Law provides for self-assessment to facilitate easy compliance and payment of taxes. It also explains the notices, the demand and recovery provisions when the taxes are unpaid, short paid and/or returns are not filed.
Broadly, the GST Procedures can be listed as:
- Audits
- Assessment
- Demand and Recovery
- Advance Ruling
Latest Update!
Now user can file RFD-01A for multiple months in a single window
1. Audits
Audit under GST is the examination of records maintained by a registered dealer. The aim is to verify the correctness of information declared, taxes paid and to assess the compliance with GST.
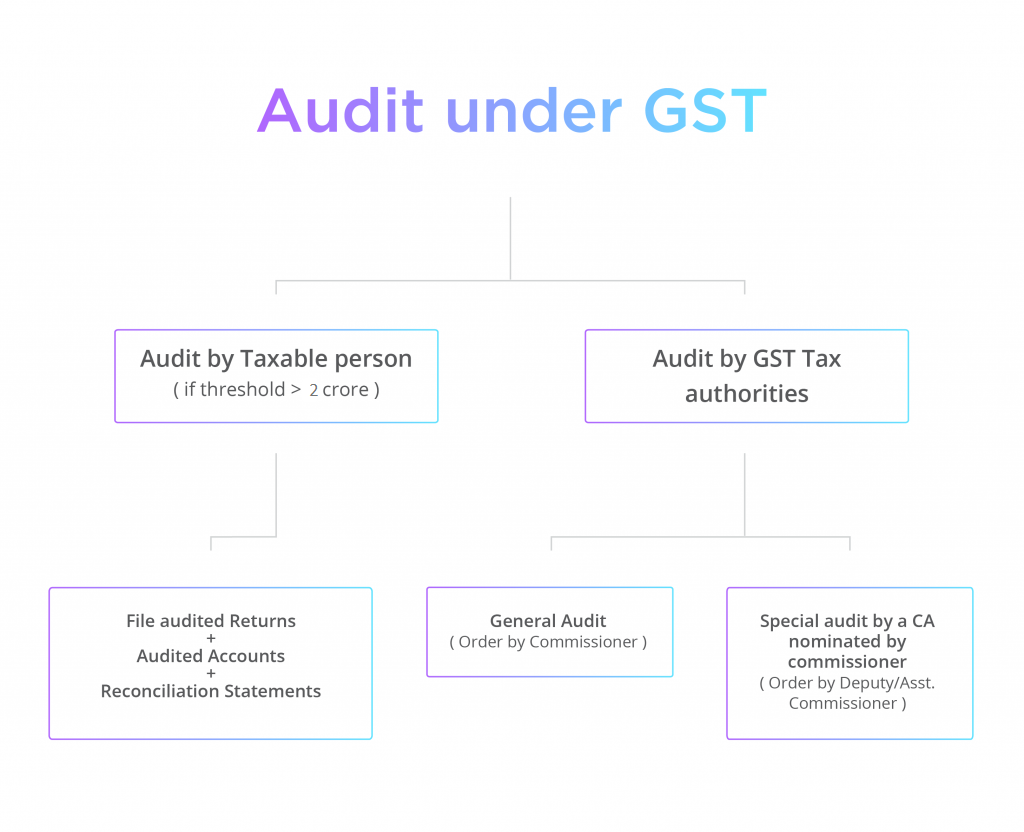 a. Audit by Registered Dealer
a. Audit by Registered Dealer
Every registered dealer whose turnover during a financial year exceeds the Rs 2 crore has to get his accounts audited by a CA or a CMA.
ICAI clarifies through an announcement dated 28th September 2018 that an Internal Auditor cannot undertake GST Audit simultaneously
b. Audit by GST Tax Authorities
General Audit: The commissioner or on his orders an officer may conduct an audit of any registered dealer.
Special Audit: The department may conduct a special audit due to the complexity of the case and considering the interest of revenue. The CA or a CMA will be appointed to conduct the audit.
2. Assessment
Assessment under GST means the determination of tax liability under GST. Assessment under GST has been divided into 5 types:
a. Self Assessment
Under GST, every registered taxable person shall assess the taxes payable by them on their own, and furnish a return for each tax period. This is called self-assessment.
b. Provisional Assessment
A registered dealer can request the officer for provisional assessment if he is unable to determine the value of goods or rate of tax. The proper officer can allow the assessee to pay tax on a provisional basis at a rate or a value specified by him.
c. Scrutiny Assessment
A GST officer can scrutinize the return to verify its correctness. The officer will ask for explanations on any discrepancies noticed in the returns.
d. Summary Assessment
Summary Assessment is done when the assessing officer comes across sufficient grounds to believe any delay in showing a tax liability can harm the interest of the revenue. To protect the interest of the revenue, he can pass the summary assessment with the prior permission of the additional/joint commissioner.
e. Best Judgement Assessment
1. Assessment of non-filers of returns
If a registered taxable person does not file his return even after getting a notice, the proper officer will assess the tax liability to the best of his judgment using the available relevant material.
2. Assessment of unregistered persons
This assessment is done when a taxable person fails to obtain registration even though he is liable to do so.
The officer will assess the tax liability of such persons to the best of his judgement. The taxable person will receive a show cause notice and an opportunity of being heard.
3. Demand and Recovery
Demand and recovery provisions are applicable when a registered dealer has paid tax incorrectly or not paid tax at all. It is also applicable when an incorrect refund or ITC is claimed by the dealer.
The proper officer will issue a show cause notice along with a demand for payment of tax and penalty in case of fraud.
1. Unpaid or short paid tax or wrong refund
2. Tax collected but not deposited with the Central or a State Government
3. CGST/SGST paid when IGST was payable and vice versa.
If demand is not paid, the GST authority starts recovery proceedings
4. Advance Ruling
Advance Ruling under GST means seeking clarifications from GST authority on certain tax matters before starting the proposed activity. This helps to reduce costly litigation.
An advance ruling is a written decision given by the tax authority to an applicant on queries related to the supply of goods/services.
Related Articles
What is GST Audit?
Need for GST Audit and meaning Audit under GST involves examination of records, returns and other documents maintained by a GST registered person. It also ensures correctness of turnover declared, taxes paid, refund claimed, input tax credit availed ...what are the GST Departmental Audit Applicability?
GST Departmental Audit GST has been one of the biggest tax reforms of our country. July 2021 marked four years of GST Implementation and though it has stabilized to a large extent, the taxpayers are still grappling with some issues and compliances ...What Do you mean by GST Audit?
GST Audit means examination of records, returns and documents maintained and furnished by registered person to check the following:- a) Verify the correctness of turnover declared. ...Latest GST News, Information, Notifications & Announcements
This section contains the latest GST updates. We regularly publish all the GST news & related information here: Latest GST News GST Council Meet Recent Notification and Circulars Latest GST News 5th May 2020 A further extension granted for filing ...Different Types Of GST Returns in India
GST returns are different forms that a taxpayer has to file for every GSTIN to which he is registered. What are GST Returns? GST Returns are a type of form that a taxpayer has to file. There are around 22 types of GST forms available. From these 22 ...